The Beginner’s Guide To Virtual Network Operators
A virtual network is a software-based network that enables devices and resources to connect and communicate over the internet or existing physical infrastructure. It simulates the functionality of traditional networks without requiring physical hardware. Virtual networks provide flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making them ideal for businesses needing remote access, secure data transmission, and seamless integration with cloud services. They allow for the creation of isolated network segments, enhancing security and resource management. By facilitating remote collaboration and centralized management, virtual networks play a crucial role in modern IT environments, supporting the dynamic needs of organizations across various industries.
What is a Virtual Network?
A virtual network is a software-defined network that allows devices, servers, and systems to communicate without relying on traditional physical infrastructure like cables, routers, or switches. Instead, it operates using cloud computing and virtualization technologies to create a flexible, scalable, and secure networking environment. Virtual networks enable remote access, seamless data transfer, and efficient resource sharing by leveraging VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), SDN (Software-Defined Networking), and cloud-based connections. Businesses use virtual networks to enhance security, improve collaboration, and integrate cloud services, making them an essential component of modern IT infrastructure. They are widely used in remote work setups, hybrid cloud environments, and IoT (Internet of Things) applications to optimize connectivity and performance.
Key features of virtual networks include:
- Software-Based Connections: Virtual networks use software to establish connections between devices, enabling flexibility and scalability.
- Isolation: They can be configured to isolate specific network segments for security or performance reasons, allowing for controlled access to resources.
- Resource Sharing: Virtual networks enable the sharing of resources like files, applications, and services across different devices and locations.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): A common example of a virtual network that provides secure, encrypted connections over the internet.
- Cloud Integration: Many virtual networks are integrated with cloud services, allowing for seamless access to cloud-based resources and services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the need for physical infrastructure, virtual networks can lower costs related to hardware, maintenance, and management.
- Dynamic Configuration: They allow for rapid configuration changes to meet evolving network needs without the need for physical changes.
What Are The Benefits Of Virtual Networking
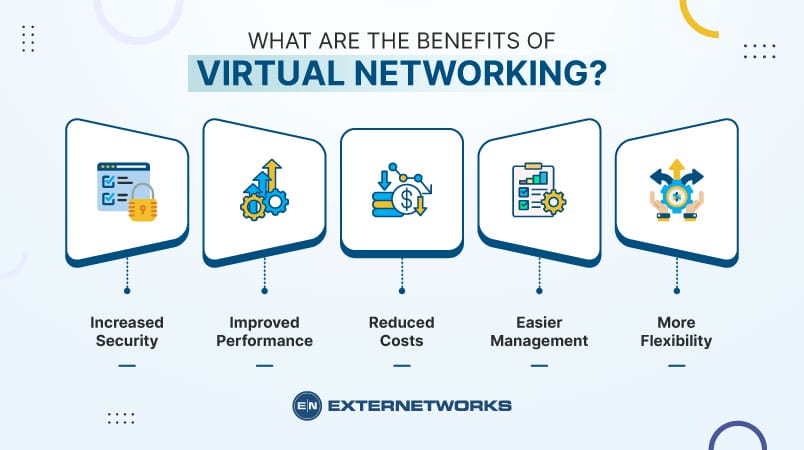
Virtual networking provides numerous advantages for businesses, organizations, and individuals by enabling seamless connectivity, flexibility, and cost efficiency. It allows for remote access, ensuring employees and teams can work from anywhere while maintaining secure connections through VPNs and cloud networks. With scalability, organizations can expand their network infrastructure without needing extensive physical hardware. Virtual networking also enhances security, integrating firewalls, encryption, and access controls to protect sensitive data. Additionally, it supports cloud computing, virtualization, and IoT, making resource allocation and management more efficient. By reducing hardware costs and maintenance, businesses can optimize operations, improve collaboration, and enhance productivity in a digital-first environment.
Key Benefits of Virtual Networking :
- Remote Access & Flexibility – Employees can securely access resources from anywhere, enhancing collaboration.
- Scalability & Cost Efficiency – Expands networks without investing in costly physical infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security – Uses encryption, firewalls, and VPNs to protect data from cyber threats.
- Cloud & IoT Integration – Supports cloud computing, virtualization, and IoT for efficient resource management.
- Simplified Network Management – Automated monitoring and centralized control improve efficiency.
- Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery – Ensures minimal downtime with cloud backups and failover systems.
Why is Virtual Networking Important?
Virtual networking is essential in today’s digital world as it enables businesses, organizations, and individuals to connect, communicate, and operate efficiently over the internet and cloud-based environments. It allows for scalability, flexibility, and cost savings by eliminating the need for physical infrastructure, making it easier to expand networks without costly hardware upgrades.
Virtual networking supports remote work, enabling employees to securely access company resources from anywhere using VPNs and cloud networks. Additionally, virtual networking enhances security and data protection through encryption, firewalls, and access controls, reducing cyber risks. It also integrates seamlessly with cloud computing, virtualization, and IoT, ensuring businesses can optimize resources and improve efficiency.
With the increasing demand for hybrid and remote work environments, virtual networking has become a critical component for organizations looking to stay competitive and connected in a globalized digital economy. By leveraging virtual networks, businesses can improve collaboration, streamline operations, and enhance overall productivity.
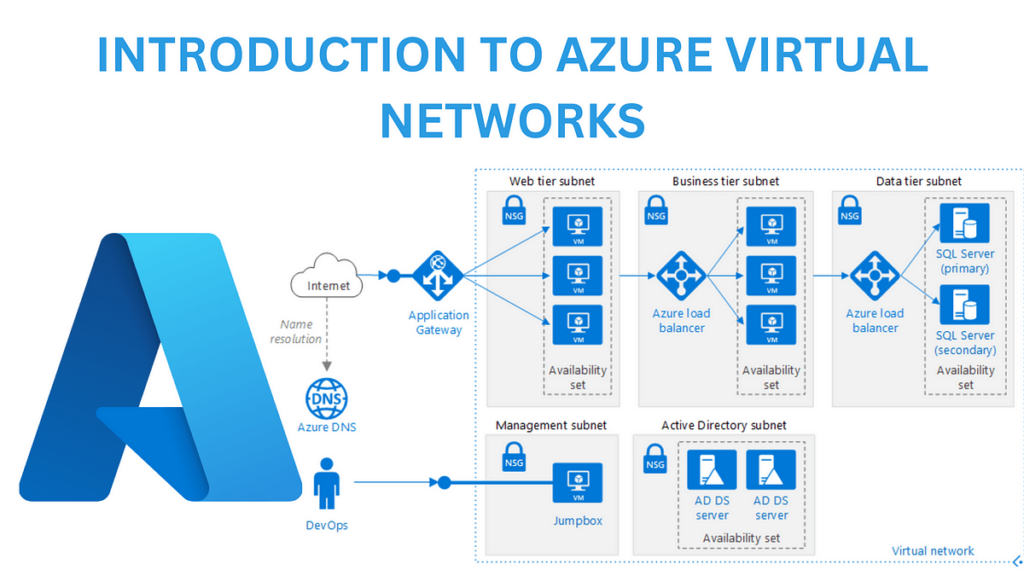
How to Configure and Manage Virtual Networks? (A Step-by-Step)

Configuring and managing virtual networks involves setting up network infrastructure using software-defined networking (SDN) to ensure seamless connectivity, security, and performance. The process starts with defining the network structure, selecting the appropriate cloud service provider, and configuring virtual network components like subnets, firewalls, and VPNs. Security policies must be implemented to protect data, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. Continuous monitoring and optimization ensure network performance, while automation tools help streamline network management. By properly configuring and managing virtual networks, businesses can achieve scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency in their IT infrastructure.
Key Steps to Configure and Manage Virtual Networks
- Define Network Architecture – Plan the virtual network structure, including subnets, IP addresses, and connectivity requirements.
- Choose a Cloud Service Provider – Select a platform like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud for virtual networking.
- Configure Virtual Network Components – Set up subnets, gateways, routers, and firewalls to manage traffic and security.
- Implement Security Policies – Use encryption, firewalls, VPNs, and access controls to protect network data.
The Different Normal Network vs Virtual Network
| Feature | Normal Network (Physical) | Virtual Network (Software-Defined) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses physical hardware (routers, switches, cables). | Software-based networking over the internet/cloud. |
| Infrastructure | Requires physical components. | Uses software & cloud with minimal hardware. |
| Scalability | Limited; needs more hardware for expansion. | Highly scalable, no physical upgrades needed. |
| Flexibility | Fixed locations; difficult to modify. | Easily modified/moved without hardware changes. |
| Security | Uses firewalls & physical access controls. | Uses encryption, firewalls, VPNs, & cloud security. |
| Setup & Maintenance | Manual setup & maintenance of hardware. | Automated updates & cloud monitoring. |
| Cost | High (hardware, installation, maintenance). | Lower (reduces hardware dependency). |
| Access | On-premises only; limited remote access. | Remote access from anywhere via cloud/VPN. |
| Performance | Consistent but needs upgrades for high demand. | Scalable; depends on cloud/server resources. |
| Use Cases | Offices, data centers, local networks. | Cloud computing, remote work, hybrid workplaces. |
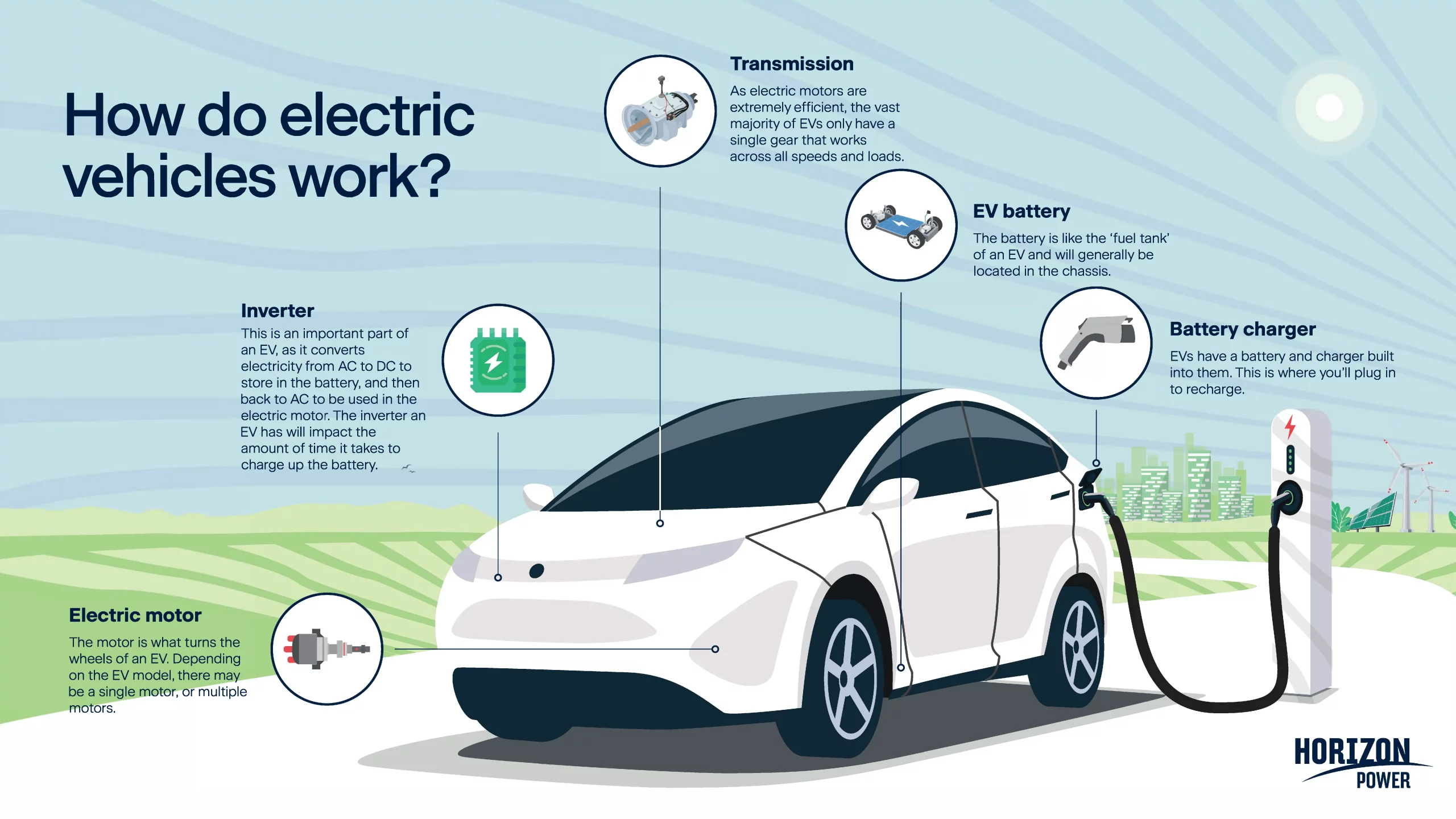
How Does Virtual Networking Work?

Virtual networking works by abstracting network hardware and functionality into software. Instead of relying on physical switches, routers, and cables, virtual networking software creates and manages virtual versions of these components.
This software layer sits on top of the physical network infrastructure and controls how data flows between virtual machines, containers, or other virtual endpoints. It uses techniques like network virtualization and software-defined networking (SDN) to create isolated virtual networks that can share the same underlying physical hardware.
Data traffic is routed and managed by these virtual components, allowing for flexible configuration, dynamic resource allocation, and simplified network management. Essentially, virtual networking creates a software-defined layer that overlays the physical network, enabling the creation and management of multiple independent and customizable networks without requiring changes to the physical infrastructure.
Advantages of Using Virtual Networks
Virtual networks offer numerous advantages that make them appealing to modern organizations seeking efficient and flexible networking solutions. One of the primary benefits is cost efficiency, as virtual networks reduce the need for extensive physical hardware, leading to significant savings in both capital expenditures and maintenance costs. They also provide exceptional scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their network size according to changing demands without the complexities associated with physical infrastructure adjustments.
Security is another critical advantage, with virtual networks offering isolated environments and advanced security features like encryption and access controls, ensuring that data is well-protected. Additionally, virtual networks optimize resource utilization by allowing for dynamic allocation and improved efficiency, which helps in reducing waste. Their flexibility supports remote access, enabling secure connections for mobile workforces and facilitating seamless integration with various cloud services and applications.
Furthermore, virtual networks enhance disaster recovery capabilities by simplifying backup processes and enabling rapid recovery in the event of failures. Their compatibility with existing systems ensures that organizations can transition smoothly without significant disruptions. Overall, virtual networks provide a robust, adaptable, and secure infrastructure that supports the dynamic needs of today’s digital landscape.
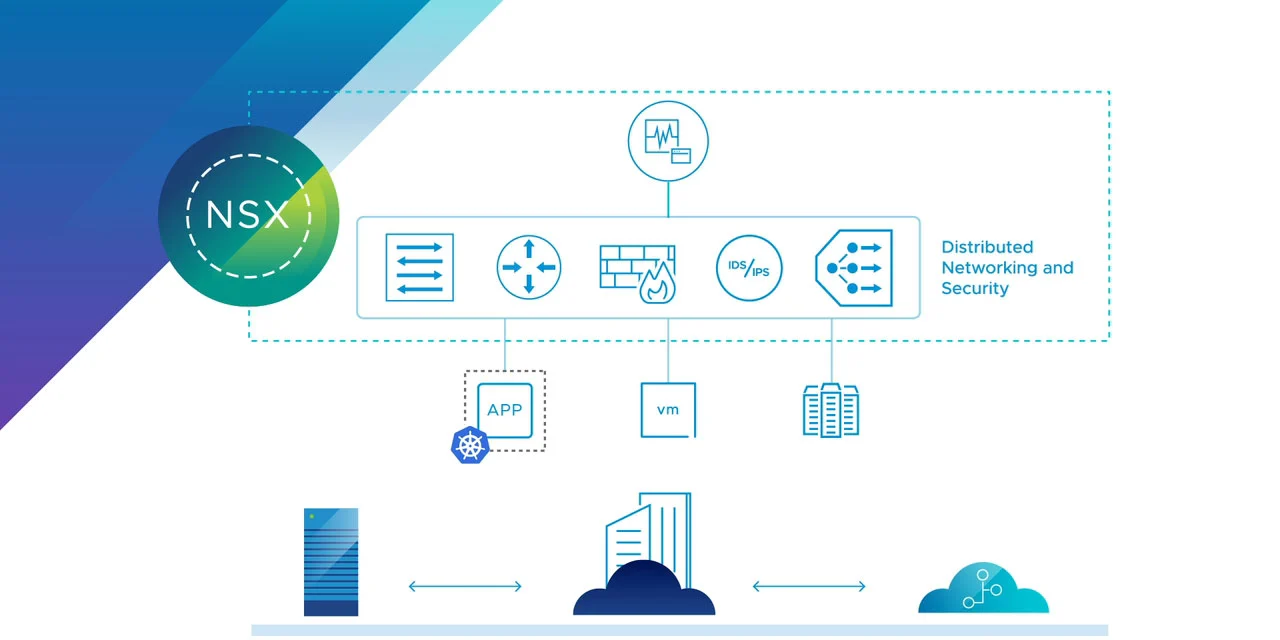
Virtual Network Security

Virtual Network Security refers to the measures and protocols used to protect data, applications, and resources within a virtualized network environment. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud computing, virtualization, and remote work, securing virtual networks has become essential to prevent cyber threats such as hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
Key components of virtual network security include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to safeguard sensitive data. Organizations also implement virtual private networks (VPNs) to ensure secure remote access and network segmentation to limit unauthorized movement within a system. Additionally, AI-driven threat detection and continuous monitoring help identify and respond to security risks in real time.
By adopting a multi-layered security approach, businesses can enhance data protection, reduce vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with cybersecurity regulations. As virtual networks continue to expand, implementing strong security strategies is crucial for maintaining business continuity and protecting digital assets.
1. What is the difference between a virtual network and a physical network?
A virtual network is a software-based network running on physical hardware, offering greater flexibility and cost-efficiency than traditional physical networks.
2. Can virtual networks be integrated with cloud services?
Yes, virtual networks are integral to cloud services, allowing seamless connectivity across cloud-based resources.
3. Are virtual networks secure?
Virtual networks can be highly secure when proper security measures, such as NSGs and encryption, are implemented.
4. How do I set up a virtual network?
Setting up a virtual network involves defining your network architecture, configuring virtual machines, switches, and routers, and implementing security protocols.
5. What are subnets in a virtual network?
Subnets are segments within a virtual network that partition the network into smaller, more manageable blocks. This organization helps improve network performance and security by controlling the flow of network traffic more efficiently.
6. How does virtual networking affect network performance?
Virtual networking can enhance network performance by optimizing routing and reducing physical constraints. However, performance depends on the underlying physical network infrastructure, virtual network configuration, and the capabilities of the virtualization technology used.
Conclusion
Virtual networks have become an essential part of modern technology, enabling businesses, organizations, and individuals to operate efficiently in a connected, digital-first world. They provide scalability, security, and flexibility, allowing seamless remote access, integration with cloud computing, and cost-effective network management. By eliminating the need for physical infrastructure, virtual networks enhance collaboration, optimize resource allocation, and improve cybersecurity through advanced encryption and firewall protection. As businesses continue to embrace remote work, cloud solutions, and IoT, virtual networking will play a crucial role in ensuring efficient communication, data transfer, and business continuity. Adopting virtual network solutions is key to staying competitive in an increasingly digital world.