Business Disaster Recovery Essential Strategies for Resilience

In today’s fast-paced world, businesses face numerous threats, from natural disasters and cyberattacks to system failures and human errors. Business disaster recovery (BDR) is a strategic plan that ensures companies can quickly recover and resume operations after an unexpected event. A strong disaster recovery plan includes data backup solutions, risk assessments, emergency response strategies, and communication protocols to minimize downtime and financial losses.
Whether it’s recovering lost data, restoring IT infrastructure, or maintaining business continuity, having a well-defined recovery strategy is crucial for long-term success. Businesses that invest in disaster recovery not only safeguard their assets but also maintain customer trust and operational resilience in the face of disruptions. This blog explores the critical strategies and measures that businesses should adopt to prepare, respond, and efficiently recover from disasters.
What is a Business Disaster Recovery?
Business Disaster Recovery (BDR) is a strategic process that enables organizations to restore operations after unexpected disruptions, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, hardware failures, or human errors. The primary goal of BDR is to minimize downtime, protect critical data, and ensure business continuity. A well-structured disaster recovery plan includes data backup and recovery solutions, ensuring that important files and systems can be restored quickly.
It also involves risk assessments, IT infrastructure recovery, and emergency response protocols to mitigate damage and resume operations efficiently. Clear communication strategies and predefined roles help businesses respond swiftly to crises. By implementing a strong disaster recovery plan, companies can reduce financial losses, maintain customer trust, and safeguard their long-term success even in the face of unexpected disruptions.

Why is Business Disaster Recovery Important?
Business Disaster Recovery (BDR) is crucial for ensuring the continuity and resilience of an organization in the face of unexpected disruptions. Disasters such as cyberattacks, natural calamities, power outages, or system failures can cause severe operational and financial losses. Without a proper recovery plan, businesses risk losing critical data, experiencing extended downtime, and damaging their reputation.
A well-structured disaster recovery plan minimizes downtime, protects sensitive data, and ensures quick restoration of IT infrastructure, allowing businesses to resume operations with minimal impact. It also helps in regulatory compliance, as many industries require companies to have data protection and continuity measures in place. Ultimately, investing in disaster recovery safeguards a business’s future, ensuring long-term stability, customer trust, and financial security.
How Business Disaster Recovery work?
Business Disaster Recovery (BDR) works by implementing a structured plan that enables an organization to quickly recover from unexpected disruptions such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or system failures. The process begins with a risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. Businesses then establish data backup solutions, ensuring that critical information is securely stored and can be restored when needed.
In the event of a disaster, IT infrastructure recovery procedures are activated to restore systems, servers, and networks. A well-defined communication plan ensures that employees, stakeholders, and customers are informed about the recovery process. Additionally, emergency response teams follow predefined protocols to minimize downtime and financial loss. Regular testing and updates of the disaster recovery plan help businesses stay prepared for evolving threats, ensuring long-term resilience and continuity.
Planning a Disaster Recovery Strategy
Planning a Disaster Recovery Strategy requires a proactive approach to minimize risks and ensure business continuity in the face of unexpected disruptions. The process begins with a risk assessment, identifying potential threats such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or hardware failures. Next, businesses must define their Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) to determine how quickly operations must resume and how much data loss is acceptable.
Implementing data backup solutions, including cloud storage and offsite backups, ensures critical information is protected. A comprehensive IT recovery plan should include restoring servers, networks, and software. Clear emergency response protocols and a communication plan help coordinate teams and inform stakeholders. Regular testing and updates of the disaster recovery strategy ensure effectiveness and preparedness for evolving threats.
Why Every Business Needs a Cybersecurity Plan
In today’s digital world, cyber threats are a growing concern for businesses of all sizes. A cybersecurity plan is essential to protect sensitive data, prevent financial losses, and maintain customer trust. Cyberattacks such as phishing, ransomware, and data breaches can lead to severe consequences, including downtime, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
A well-structured cybersecurity plan includes firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular software updates, and employee training to mitigate risks. Businesses also need incident response protocols to detect and respond to security breaches effectively. With cyber threats evolving constantly, having a proactive cybersecurity strategy ensures business continuity, safeguards digital assets, and strengthens overall resilience against potential attacks.
Types of Business Disaster Recovery
Businesses must implement different disaster recovery strategies based on their needs, IT infrastructure, and risk exposure. Below are the key types of Business Disaster Recovery (BDR):
1. Data Backup and Recovery: One of the most fundamental disaster recovery strategies, data backup and recovery, involves regularly backing up business-critical data to secure locations. These backups can be stored in cloud storage, external drives, or offsite data centers. In case of a cyberattack, system failure, or accidental data loss, businesses can quickly restore essential files and resume operations. Regularly testing backup restoration ensures that data recovery is efficient when needed.
2. Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery: Cloud disaster recovery leverages cloud services to store and restore business data and applications. This method provides scalability, remote access, and automated backups without the need for expensive on-site infrastructure. In the event of a disaster, businesses can quickly recover their systems using cloud backups, ensuring minimal downtime and cost-effective disaster management.
3. Virtualization-Based Recovery: Virtualization technology creates replicas of business systems, allowing businesses to run operations on virtual machines (VMs) in case of a hardware failure or cyberattack. Virtualized backups enable organizations to quickly switch to a replica environment, reducing downtime and ensuring continuity. Since virtual environments can be restored almost instantly, this approach is highly effective for maintaining workflow during disruptions.
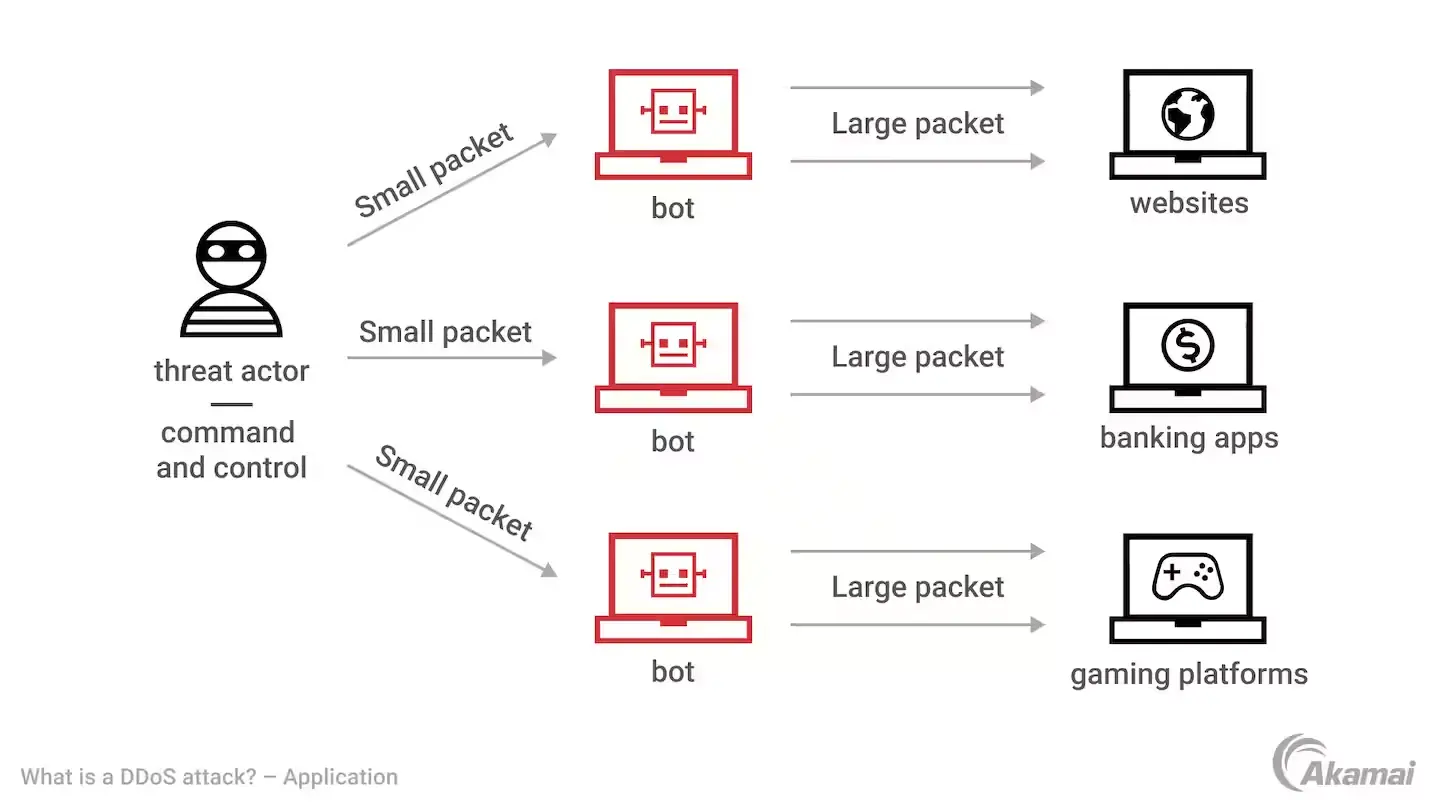
4. Network Disaster Recovery: For businesses relying on digital connectivity, network disaster recovery is crucial. This strategy involves backup networking systems, redundant network infrastructure, and failover mechanisms to restore connectivity in case of cyberattacks, hardware failures, or power outages. Organizations implement alternative communication channels and secondary networks to ensure that business operations continue without major disruptions.
5. Disaster Recovery as a Service: Disaster recovery as a service is a cloud-based service where a third-party provider manages disaster recovery for a business. This approach allows companies to recover their applications, data, and entire IT infrastructure remotely in the event of a disaster. Disaster recovery as a service offers automated failover solutions, making it ideal for businesses that want a cost-effective, hands-free approach to disaster recovery.
6. Cold, Warm, and Hot Site Recovery: Businesses can maintain alternative sites to ensure business continuity during disasters. A cold site is a secondary location with minimal infrastructure, requiring more time to set up after a disruption. A warm site is a partially configured backup office with essential systems, allowing for faster recovery. A hot site is a fully operational backup office with real-time data synchronization, ensuring immediate business continuity with no downtime. Businesses choose a site recovery option based on their recovery time objectives (RTO).
7. Hybrid Disaster Recovery: A hybrid disaster recovery strategy combines on-premises and cloud-based solutions to provide maximum flexibility and reliability. This approach allows businesses to store data locally for quick recovery while also maintaining cloud backups for added security and long-term storage. Hybrid solutions ensure that businesses can recover from various types of disasters, including cyberattacks, hardware failures, and natural disasters.
Each business should assess its risks, budget, and operational needs to determine the most suitable disaster recovery strategy. Implementing a proactive and well-tested disaster recovery plan is essential to minimize downtime, reduce financial loss, and maintain business continuity in any unforeseen event.
Benefits of Business Disaster Recovery
Business disaster recovery (BDR) is crucial for ensuring continuity, minimizing downtime, and protecting valuable assets during unexpected disruptions. Here are some key benefits:
- Minimizes Downtime: Helps businesses quickly recover from disasters (cyberattacks, power failures, natural disasters) and resume operations without significant delays.
- Protects Data & Assets: Ensures critical business data is backed up and can be restored in case of hardware failure, cyberattacks, or accidental deletion.
- Enhances Business Continuity: Keeps essential operations running even during crises, preventing loss of revenue and maintaining customer trust.
- Reduces Financial Losses: Downtime and data loss can be expensive. A well-planned disaster recovery strategy helps mitigate financial risks associated with disruptions.
- Improves Cybersecurity: Protects against ransomware, malware, and hacking attempts by enabling quick data recovery and minimizing exposure.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Many industries (finance, healthcare, e-commerce) require businesses to have backup and recovery solutions to comply with legal and security standards.
- Boosts Customer Confidence: Customers trust businesses that can handle crises effectively. A solid disaster recovery plan reassures clients that their data and services are safe.
- Increases Competitive Advantage: Companies with strong disaster recovery plans can maintain service availability while competitors struggle with disruptions.
- Supports Remote Work & Flexibility: Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions ensure employees can access data and systems from anywhere, keeping the business operational.
- Prepares for Unforeseen Events: Natural disasters, cyberattacks, or system failures can happen anytime. A disaster recovery plan ensures the business is always prepared.
Frequently Asked Question
Here are some frequently asked question about business disaster recovery:
What is Business Disaster Recovery, and why is it important?
Business Disaster Recovery (BDR) is a strategic plan that ensures businesses can recover operations quickly after unexpected disruptions such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or system failures. It is essential to minimize downtime, protect critical data, and maintain business continuity.
What are the key components of a Disaster Recovery Plan?
A disaster recovery plan includes risk assessment, data backup strategies, IT infrastructure recovery, incident response protocols, cybersecurity measures, employee training, and regular testing to ensure businesses can recover effectively from disruptions.
How often should a Disaster Recovery Plan be tested?
A disaster recovery plan should be tested at least once a year or whenever significant changes occur in business operations, IT infrastructure, or cybersecurity threats. Regular testing helps identify weaknesses and ensures that the recovery strategy remains effective.
What are the best backup strategies for disaster recovery?
The best backup strategies include cloud-based backups, offsite data storage, automated backup systems, and redundant storage solutions. Businesses should follow the 3-2-1 backup rule (three copies of data, stored in two different mediums, with one copy offsite) for maximum protection.
How does Disaster Recovery differ from Business Continuity?
Disaster Recovery (DR) focuses on restoring IT infrastructure, data, and critical systems after a disruption, whereas Business Continuity (BC) ensures that all essential business operations continue during and after a disaster. DR is a key part of BC, but BC covers a broader scope, including workforce management, alternative operations, and long-term recovery.
Conclusion
Business Disaster Recovery is not just about responding to crises but about proactively preparing to ensure that your business can withstand and quickly recover from unexpected events. By understanding the essentials of disaster recovery planning and implementing a robust plan, companies can protect themselves against significant losses, maintain continuity, and secure a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced business environment. Investing in disaster recovery is investing in your business’s future.
By embracing these strategies, organizations can navigate the complexities of disaster recovery and ensure operational resilience, no matter what challenges lie ahead.