Cyber Danger Understanding and Battling Online Threats

In today’s digital world, online threats have become a serious concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. As our lives become increasingly connected through the internet, the risk of cyberattacks continues to grow. From phishing scams and ransomware to data breaches and identity theft, these threats can cause significant damage financially, emotionally, and reputationally. Hackers are constantly developing new tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and human behavior.
Whether you’re browsing social media, checking emails, or managing online accounts, staying informed about these dangers is essential. Understanding the different types of online threats and how they work is the first step in protecting yourself and your information in the digital space. Cybersecurity is no longer optional it’s a necessity.
What Are Online Threats?
Online threats refer to malicious activities or dangers that exist on the internet, aiming to harm users, steal data, or disrupt systems. These dangers can take many forms, including viruses, phishing scams, ransomware, spyware, and cyberattacks. They often target personal information, financial data, or sensitive business content. As more people rely on digital platforms for work, communication, and entertainment, the risk of exposure increases. Being aware and practicing safe online threats habits is essential to reduce vulnerability and stay protected.

How to Protect Yourself from Online Threats
1. Use Strong and Unique Passwords: Always create strong passwords using a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using the same password across multiple accounts. Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords, so you don’t have to remember them all.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring not just your password but also a second verification step, like a code sent to your phone or an authentication app. It significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access even if your password gets stolen.
3. Keep Your Software and Devices Updated: Always update your operating system, apps, antivirus software, and browsers. Developers release updates to fix security bugs and vulnerabilities. Delaying updates leaves your devices open to known threats.
4. Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Use trusted security software to detect and block threats such as viruses, ransomware, spyware, and more. Make sure the software stays updated and run regular scans to ensure your device is safe.
5. Be Cautious with Emails and Links: Do not open suspicious emails or click on unknown links. Phishing emails often look like they’re from legitimate companies but contain malicious links or attachments. Always verify the sender’s email address and avoid clicking on offers that seem too good to be true.
6. Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Transactions: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them a hotspot for hackers. Avoid logging into bank accounts or making purchases when connected to public Wi-Fi. If necessary, use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your connection.
7. Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network): A VPN hides your IP address and encrypts your internet traffic, making it harder for hackers to track your online activities. It’s especially useful when accessing the internet on public or shared networks.
8. Be Mindful of What You Share Online: Avoid sharing personal information such as your address, phone number, or financial details on social media or unfamiliar websites. Cybercriminals can use this information for identity theft or scams.
9. Download Apps and Software Only from Trusted Sources: Stick to official app stores like Google Play or the Apple App Store, and avoid downloading software from random websites. Pirated or cracked software can contain hidden malware.
10. Educate Yourself and Stay Informed: Cyber threats evolve constantly. Stay informed about the latest threats and scams. Follow cybersecurity blogs or news pages, and educate yourself and your family members about safe online threats practices.
Types of Online Threats
Phishing Attacks
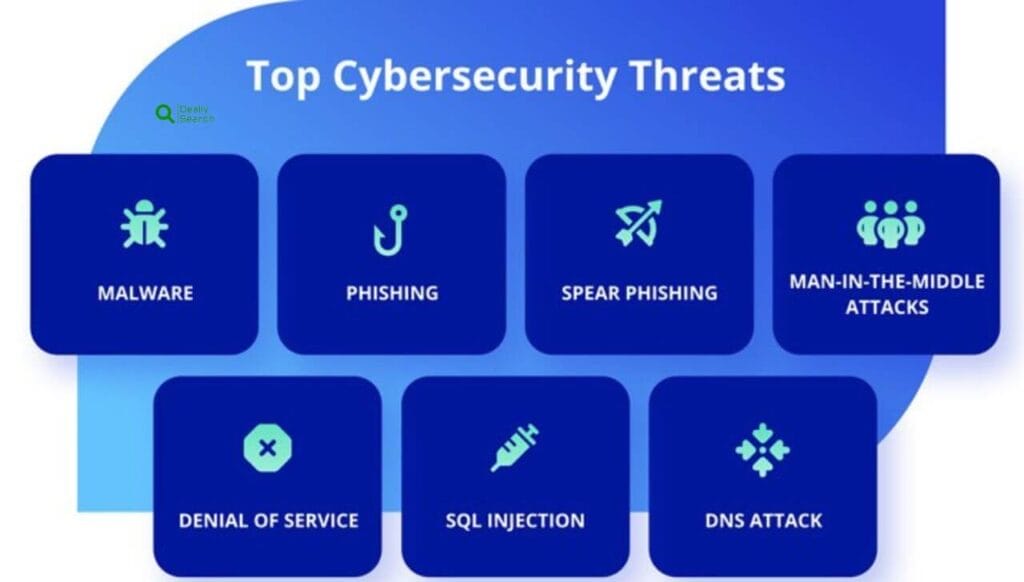
Phishing is one of the most common online threats where attackers trick users into revealing sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details. This is often done through fake emails, websites, or messages that appear to come from trusted sources. These scams usually create a sense of urgency, prompting users to click malicious links or download harmful files.
Malware (Malicious Software)
Malware refers to any software designed to harm or exploit a device or network. Common types include viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware. Malware can be spread through infected downloads, email attachments, or unsafe websites. Once installed, it can steal data, damage files, or give attackers control over the system.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that locks or encrypts a user’s data and demands payment (ransom) to restore access. Victims are usually instructed to pay in cryptocurrency. Even if the ransom is paid, there’s no guarantee the data will be recovered. Ransomware attacks target individuals, businesses, and even governments.
Spyware
Spyware secretly monitors user activity and gathers information without their knowledge. It can track keystrokes, capture screenshots, and record browsing history. This data is often sent to cybercriminals who use it for identity theft or financial fraud. Spyware can be bundled with free software or hidden in malicious links.
Adware
Adware displays unwanted advertisements on your device, often in the form of pop-ups or banners. While some adware is relatively harmless, others can slow down your device, track browsing habits, or redirect you to unsafe websites. It’s often bundled with free apps or downloaded unknowingly.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
In MitM attacks, hackers secretly intercept and possibly alter communication between two parties. This often happens on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks. By pretending to be a trusted connection, attackers can steal login credentials, financial data, or personal messages.
SQL Injection
SQL injection is a technique where hackers exploit vulnerabilities in a website’s database by inserting malicious SQL code. This can allow them to view, change, or delete sensitive data, and in some cases, take full control of the server. Poorly coded websites are especially vulnerable.
Zero-Day Exploits
These are attacks that take advantage of unknown or unpatched software vulnerabilities. Since the software developers are unaware of the flaw, there is no fix available at the time of the attack. Zero-day exploits are highly dangerous and are often used in targeted cyberattacks.
Social Engineering
This type of threat involves manipulating people into giving away confidential information. It relies more on human psychology than technical hacking. Common examples include impersonation, baiting (leaving infected devices for others to find), and pretexting (pretending to need information for a legitimate reason).
Future Trends in Online Threats
The landscape of online threats is rapidly evolving, with several emerging trends posing significant challenges to cybersecurity:
AI-Driven Cyberattacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the sophistication and effectiveness of their attacks. AI enables the automation of complex tasks such as crafting convincing phishing emails, developing adaptive malware, and executing large-scale attacks with greater precision. This evolution allows attackers to bypass traditional security measures more effectively, necessitating advanced defense strategies.
Deepfake and Synthetic Media: The advent of deepfake technology has introduced new dimensions to online threats. By creating highly realistic synthetic audio and video content, malicious actors can impersonate individuals, spread misinformation, and conduct sophisticated fraud schemes. These capabilities undermine trust in digital media and present significant challenges for verification processes.
Quantum Computing Threats: Advancements in quantum computing pose potential risks to current encryption standards. Quantum computers could, in the future, break widely used cryptographic algorithms, compromising the security of sensitive data. Organizations are advised to prepare for this eventuality by developing and implementing quantum-resistant encryption methods.
Cyber-Physical System Vulnerabilities: The integration of digital systems with physical infrastructure such as in smart grids, autonomous vehicles, and industrial control systems has expanded the attack surface for cyber threats. Compromises in these cyber-physical systems can lead to tangible, real-world consequences, including physical damage and threats to human safety.
Supply Chain Attacks: Attackers are increasingly targeting supply chains to infiltrate organizations. By compromising less-secure elements within a supply network, cybercriminals can gain access to larger, more secure targets. This tactic exploits the interconnectedness of modern business ecosystems, making it imperative for organizations to assess and secure their entire supply chain.
Frequently Asked Question
Hear are some frequently asked question about online threats
What are online threats?
Online threats are malicious activities that occur on the internet, aiming to steal data, harm systems, or exploit users. These include viruses, phishing, ransomware, and hacking attempts that target individuals, businesses, and government systems.
How can I recognize a phishing attempt?
Phishing attempts often appear as emails or messages that look official, asking you to click links or provide sensitive information. Watch for poor grammar, urgent language, or suspicious URLs that don’t match the company’s official site.
What should I do if I suspect a cyberattack?
Immediately disconnect from the internet, run a full antivirus scan, change your passwords, and report the incident to your IT department or a cybersecurity expert. Acting quickly can reduce potential damage and prevent further access.
Are mobile devices at risk from online threats?
Yes, mobile devices can be targeted by malware, phishing, and malicious apps. Always use official app stores, avoid suspicious links, and keep your device’s software up to date to reduce the risk of attack.
What is ransomware and how does it work?
Ransomware is a type of malware that locks your files or system and demands payment to unlock them. It often spreads through email attachments or compromised websites, and paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee your data’s return.
How often should I update my software?
You should update your software as soon as updates are available. These updates often fix security vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Enabling automatic updates helps ensure your system remains protected against the latest threats.
Why is cybersecurity awareness important?
Cybersecurity awareness helps individuals recognize threats, avoid risky behavior, and protect personal and organizational data. An informed user is less likely to fall for scams or make mistakes that could lead to major security breaches.
Related Post: Ensuring Business Continuity: The Imperative of Data Security Management
Conclusion
Online threats continue to evolve, posing serious risks to individuals, businesses, and society at large. From sophisticated phishing scams to AI-powered attacks and ransomware, cybercriminals are becoming smarter and more strategic. As our reliance on digital platforms increases, so does our exposure to these dangers. It is no longer enough to rely solely on antivirus software or firewalls cybersecurity requires awareness, proactive behavior, and constant vigilance.
By staying informed, practicing safe online habits, and updating our defenses regularly, we can significantly reduce our vulnerability. Everyone has a role to play in protecting the digital world. In this fast-paced, tech-driven era, staying one step ahead of online threats is not just a safety measure it’s a necessity for a secure future.