Securing Your Digital World Embracing Multi-Factor Strong Authentication

In today’s digital world, cyber threats are increasing at an alarming rate. According to recent reports, over 80% of data breaches happen due to weak or stolen passwords. With the rise of online banking, social media, and e-commerce, securing personal and business accounts is more important than ever. Strong authentication is the key to preventing identity theft, fraud, and cyberattacks. Big companies like Google, Apple, and Microsoft now encourage multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security. This article explores why strong authentication matters, how it works, and the best ways to protect your online presence. Whether you’re an individual user or a business owner, understanding this concept can help you stay ahead of cybercriminals and keep your sensitive information safe.
What is a Strong Authentication?

Strong authentication is a way to keep online accounts and personal information safe by making sure only the right person can access them. Normally, when logging into an account, people use a password. But passwords can be stolen, guessed, or hacked. That’s why strong authentication adds extra layers of security. It requires two or more steps to prove that you are you. One common way is using two-factor authentication (2FA). After entering your password, you must also enter a special code sent to your phone or email. Some websites or apps might even ask you to scan your fingerprint, use face recognition, or answer a secret question.
Think of strong authentication like a treasure chest with two locks. If a thief finds one key, they still can’t open it without the second one. This makes it much harder for hackers to break in and steal important information like bank details, emails, or social media accounts. Businesses, schools, and even video game accounts use strong authentication to protect users from cyber threats.
Many people use strong authentication without even realizing it. Logging into a website and receiving a text message with a code is a form of strong authentication. Even unlocking your phone with a fingerprint or a PIN is an example! While it might take a few extra seconds, it’s worth it to stay safe online. By using strong authentication, people can protect themselves from hackers, scammers, and other online dangers.
How Strong Authentication Works?
Strong authentication works by adding extra layers of security to make sure that only the real owner of an account can access it. Instead of just relying on a password, strong authentication requires at least two different ways to verify a user’s identity. This is often called two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) because it uses multiple steps to confirm who you are.
There are three main types of authentication factors:
- Something You Know – This is usually a password, a PIN, or the answer to a security question.
- Something You Have – This could be a code sent to your phone, an authentication app, or a security key.
- Something You Are – This includes biometric methods like fingerprint scans, face recognition, or even voice recognition.
For example, when you try to log into your email, you first enter your password (something you know). Then, the system sends a one-time code to your phone (something you have). You must enter that code to complete the login. Even if a hacker steals your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second step.
Some advanced systems use biometric authentication, like unlocking a phone with a fingerprint or face scan. Businesses and banks often use security keys or authentication apps for even stronger protection. By using multiple layers of authentication, strong authentication makes it much harder for hackers to break into accounts, keeping personal and sensitive information safe from cyber threats.
What are the types of Strong Authentication?

Strong authentication helps protect online accounts by requiring more than just a password. It uses multiple steps to verify a user’s identity, making it harder for hackers to gain access. There are different types of strong authentication, each providing extra security in its own way. One common type is two-factor authentication (2FA), where users must enter a password and then verify their identity using another method, such as a one-time code sent to their phone.
Another type is multi-factor authentication (MFA), which goes beyond two factors and may include biometrics or security keys. Biometric authentication is also widely used and includes fingerprint scans, face recognition, and even voice recognition to confirm identity. Some platforms use hardware security keys, which are physical devices that users must plug into their computer or tap against their phone to authenticate.
Authentication apps, like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, generate temporary codes that users must enter to log in, providing a safer alternative to text message codes. These different types of strong authentication work together to keep online accounts safe from cyber threats.
Key Types of Strong Authentication:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) – Requires a password plus one extra step, like a code sent to a phone.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Uses more than two security steps for extra protection.
- Biometric Authentication – Uses fingerprints, face recognition, or voice scans.
- Hardware Security Keys – Physical devices that provide an extra layer of security.
- Authentication Apps – Generate secure one-time codes instead of using text messages.
Why Strong Authentication Matters?
Strong authentication is important because it helps protect personal and sensitive information from hackers, scammers, and cybercriminals. In today’s digital world, people use online accounts for banking, shopping, social media, school, and even entertainment. Without strong authentication, these accounts can be easily hacked if someone steals or guesses a password.
If that happens, personal data, money, and private messages can be stolen or misused. Using strong authentication adds extra security by requiring more than just a password to log in. This could be a special code sent to a phone, a fingerprint scan, or even face recognition. These extra steps make it much harder for hackers to break into accounts, even if they somehow get the password.
It’s like having a strong lock on a door that needs both a key and a secret code to open. Cybercriminals often use tricks like phishing, where they send fake emails or messages to steal passwords. With strong authentication, even if someone falls for a scam and gives away their password, the hacker still won’t be able to access the account without the second security step.
Many big companies, banks, and schools now require strong authentication to keep users safe. While it may take a few extra seconds to log in, it is worth it to protect important information. By using strong authentication, people can keep their accounts safe, avoid identity theft, and enjoy a more secure online experience.
How to Make Authentication Strong?
To keep online accounts safe, it’s important to make authentication as strong as possible. The best way to do this is by using two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever it is available. This means that instead of just entering a password, you need to take an extra step to prove your identity. For example, after typing in your password, you might get a special code sent to your phone or email that you must enter before logging in. This makes it much harder for hackers to break into your account, even if they somehow steal your password.
Another way to strengthen authentication is by using strong and unique passwords. Instead of using simple passwords like “123456” or “password,” create a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols. Each account should have a different password so that if one gets stolen, the others stay safe. A password manager can help store and organize passwords securely.
If possible, use biometric authentication, such as fingerprint scans or face recognition, for an extra layer of protection. These are harder to steal than passwords. Also, avoid using text messages for authentication when possible—authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator are safer. Finally, always watch out for scams and phishing attacks. Never enter your login details on suspicious websites or share them with anyone. By following these steps, you can make authentication much stronger and keep your personal information safe from hackers.
The Importance of Strong Authentication in Cybersecurity
In today’s digital world, cybersecurity is more important than ever. People use the internet for banking, shopping, social media, gaming, and even schoolwork. However, hackers and cybercriminals are always looking for ways to steal personal information, money, and private data. This is where strong authentication plays a key role in keeping people safe online.
Strong authentication goes beyond just using a password. It adds extra security steps, like two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA), to make sure that only the real owner of an account can access it. This can include a code sent to a phone, a fingerprint scan, or face recognition. Even if a hacker guesses or steals a password, they won’t be able to log in without the second security step.
Cybercriminals often use tricks like phishing, where they send fake emails or messages pretending to be from a trusted company. They try to trick people into entering their passwords on fake websites. With strong authentication, even if someone accidentally shares their password, the hacker still won’t be able to access their account without the second authentication step.
Many companies, banks, and social media platforms now require strong authentication to protect their users. While it might take a few extra seconds to log in, it’s worth it to prevent identity theft, financial loss, and data breaches. By using strong authentication, people can stay safer online, protect their accounts, and reduce the risk of cyberattacks. It is a simple but powerful way to improve cybersecurity.
Best Practices for Strong Authentication
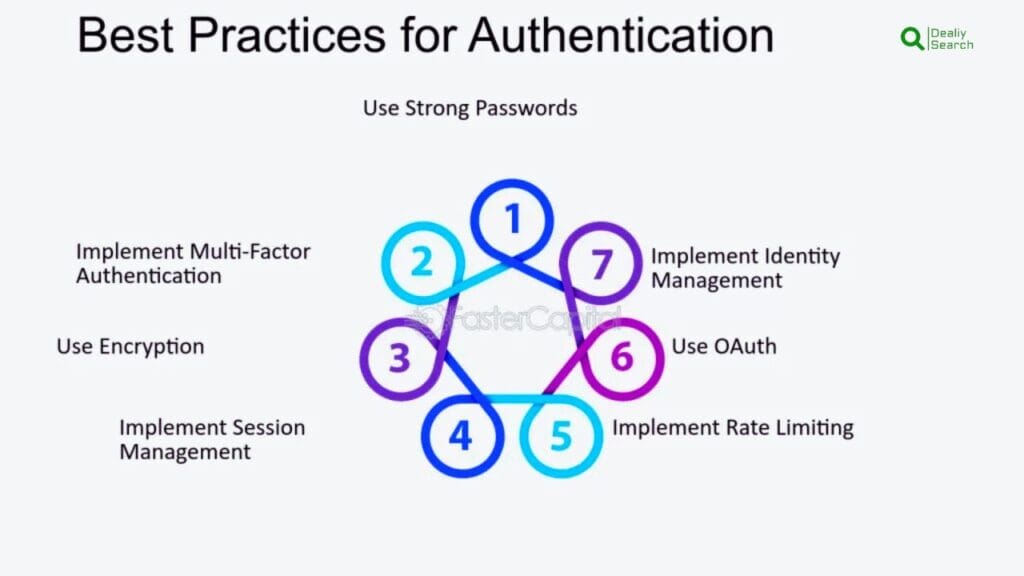
Strong authentication helps keep online accounts safe, but to make it even stronger, it’s important to follow some best practices. First, always turn on two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) if a website offers it. This means that after entering your password, you’ll need to confirm your identity with a code sent to your phone, an authentication app, or a fingerprint scan. This makes it much harder for hackers to break into your account.
Next, use strong and unique passwords for every account. Avoid simple passwords like “123456” or “password.” Instead, create passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols. If it’s hard to remember all your passwords, use a password manager to store them safely.
Be careful of phishing scams, where hackers try to trick you into giving them your login details through fake emails or websites. Always double-check links before clicking, and never share your password with anyone. It’s also safer to use an authentication app (like Google Authenticator) instead of text messages for 2FA because hackers can sometimes steal SMS codes.
Another great way to stay safe is to enable biometric authentication, like fingerprint or face recognition, whenever possible. Also, update your devices and apps regularly to fix security issues that hackers might exploit. By following these best practices, you can keep your accounts safe from hackers and enjoy a more secure online experience. Staying alert and using strong authentication makes a big difference in protecting personal information.
Frequently Asked Question
1. What is strong authentication?
Strong authentication is a security process that requires multiple methods of verifying a user’s identity before granting access to an account or system. This approach enhances security by combining two or more independent authentication factors, such as something you know (password), something you have (security token), or something you are (biometric data).
2. Why is strong authentication important?
Strong authentication significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. By requiring multiple forms of verification, it adds layers of security that protect sensitive information, even if one authentication factor is compromised.
3. Are there any drawbacks to using strong authentication?
While strong authentication enhances security, it can introduce minor inconveniences, such as the need for additional steps during login or reliance on specific devices for authentication. However, these are generally outweighed by the significant security benefits provided.
4. Is strong authentication necessary for all my accounts?
It’s particularly important to use strong authentication for accounts containing sensitive information, such as email, banking, and social media accounts. Implementing it across all accounts further enhances overall security.
5.How does strong authentication differ from regular authentication?
Regular authentication typically relies on a single factor, like a password. Strong authentication, on the other hand, incorporates multiple factors, making it significantly more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access. For example, even if someone knows your password, they would also need access to your physical device or biometric information to authenticate successfully.
Conclusion
Strong authentication is no longer a luxury, but a necessity in today’s digital landscape. By moving beyond simple passwords and embracing multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, or other robust methods, we significantly strengthen the barriers against unauthorized access. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and other cybercrimes, fostering a more secure and trustworthy online environment. Ultimately, strong authentication empowers individuals and organizations to confidently navigate the digital world, knowing their sensitive information is well-protected.