Security Measures Providing every merchant with the necessary

Security measures are essential strategies employed to protect information, assets, and individuals from various threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and physical intrusions. In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, these measures encompass a range of practices such as physical security, cybersecurity, information security, and personal safety protocols. By implementing comprehensive security strategies, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, maintain operational integrity, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. For individuals, security measures provide protection of personal information and privacy. Overall, effective security practices are crucial for building trust, preventing potential threats, and ensuring the resilience and success of both organizations and individuals.

What is a security measure?
Security measures are necessary to protect sensitive information, prevent unauthorized access, and safeguard businesses and individuals from cyber threats. In today’s digital world, data breaches, identity theft, and financial fraud are increasing, making strong security protocols essential. Implementing security measures such as encryption, firewalls, two-factor authentication, and regular system updates helps prevent hacking and data leaks.
For businesses, security is crucial in protecting customer data, maintaining trust, and complying with legal regulations. Without proper security, companies risk financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. By prioritizing security measures, organizations can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
Some other things are mentioned
Physical security: Measures to protect physical assets like buildings, equipment, and inventory from theft, damage, or unauthorized access. Examples include locks, security cameras, and security guards.
Cybersecurity: Measures to protect computer systems and networks from cyberattacks, malware, and data breaches. Examples include firewalls, antivirus software, and strong passwords.
Information security: Measures to protect sensitive information, whether it’s stored digitally or in paper form. Examples include encryption, access controls, and data backup procedures.
Personal safety: Measures to protect individuals from harm or injury. Examples include safety training, personal protective equipment, and emergency procedures.
Detective measures: Aim to detect security incidents as they occur. Examples include intrusion detection systems, security cameras, and audit logs.
Corrective measures: Aim to minimize the impact of security incidents and restore systems to normal operation. Examples include data recovery procedures, incident response plans, and business continuity plans.
Why is security measure necessary?
Security measures are essential to protect sensitive information, assets, and people from potential threats and unauthorized access. In today’s digital age, businesses and individuals face numerous security risks, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and physical intrusions. Implementing robust security protocols helps safeguard confidential information, such as financial data, personal records, and intellectual property, from malicious actors who may seek to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or other harmful purposes.
Security measures also ensure the integrity and availability of information systems, allowing organizations to operate without disruption and maintain trust with clients and stakeholders. Additionally, they help in complying with legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy, avoiding potential penalties and reputational damage. For individuals, security measures provide peace of mind by protecting personal safety and privacy in both physical and digital environments. Overall, investing in comprehensive security strategies is crucial for mitigating risks, preserving trust, and ensuring the continuity of operations.
How many types of security measures
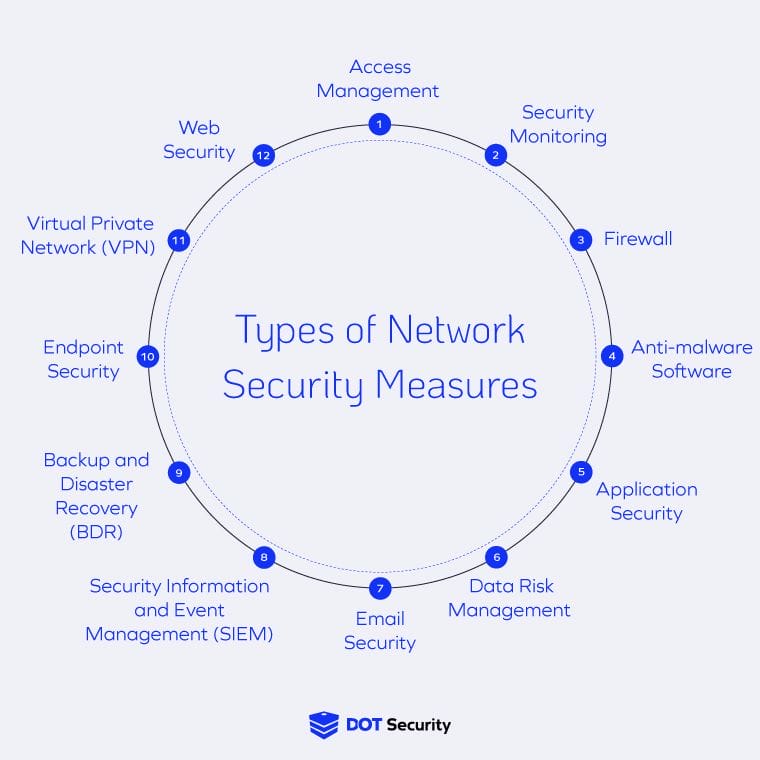
Security measures are diverse and can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving to protect against various threats and vulnerabilities. Firstly, physical security measures include locks, surveillance cameras, security personnel, and access control systems that protect physical spaces from unauthorized access and theft. Secondly, cybersecurity measures are designed to safeguard digital information and networks, encompassing firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems.
These tools help protect against cyberattacks such as hacking, malware, and phishing. Thirdly, information security measures focus on protecting sensitive data through policies and procedures like data classification, access controls, and regular audits to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. Additionally, operational security measures involve processes and practices that secure day-to-day operations, including employee training, incident response planning, and risk management strategies.
Finally, personal security measures are steps individuals take to protect themselves, such as using strong passwords and being vigilant about sharing personal information. Each type of security measure plays a vital role in creating a comprehensive defense strategy to protect assets and information across various environments.
Here are the key points regarding the types of security measures:
- Physical Security Measures
- Cybersecurity Measures
- Information Security Measures
- Operational Security Measures
- Personal Security Measures
Advanced Security Measures for Enhanced Protection
Advanced security measures are essential for ensuring enhanced protection against cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Businesses and individuals must implement multi-layered security strategies, including encryption to protect sensitive data, multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized logins, and advanced firewalls to block malicious attacks.
Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven threat detection systems provide real-time monitoring and automated responses to security incidents. Additionally, secure cloud storage, biometric authentication, and data backup solutions enhance protection against cyber risks. By adopting these advanced security measures, organizations can safeguard critical assets, maintain compliance, and prevent financial and reputational losses.
How To Increase Staff Awareness Of Security Measures
Increasing staff awareness of security measures is paramount in today’s threat landscape. It requires a multi-faceted approach that begins with cultivating a security-conscious culture, where security is not just an IT concern but a shared responsibility. Regular, engaging training programs, utilizing diverse formats like interactive workshops, real-world case studies, and microlearning modules, are crucial for educating employees on best practices.
Communication should be clear, concise, and frequent, reinforcing key messages through various channels such as newsletters, intranet posts, and visual reminders. Practical measures, like strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and regular phishing simulations, should be implemented and consistently emphasized. Furthermore, fostering open communication, where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activity, is essential.
Security awareness should be ongoing, with regular assessments and feedback mechanisms to ensure its effectiveness and adapt to evolving threats. Ultimately, by empowering employees with knowledge and promoting a proactive security mindset, organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses against cyber risks.
Implementing Security in the App Development Lifecycle
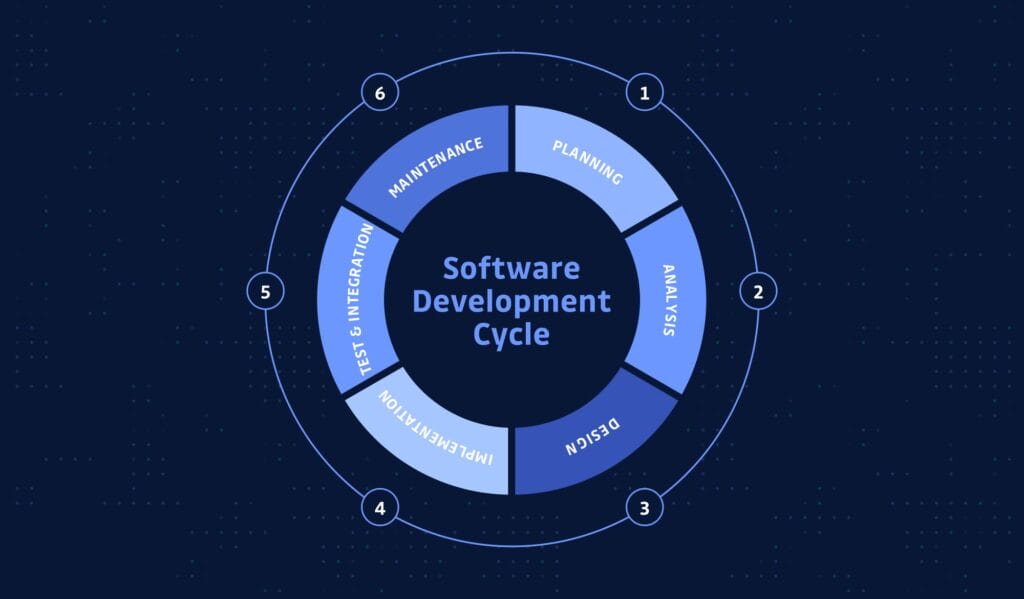
Implementing security in the app development lifecycle is essential to protect applications from potential threats and vulnerabilities. The process begins in the planning phase, where security requirements are defined, and a risk assessment is conducted to identify potential threats. During the design phase, secure architecture principles like least privilege and defense-in-depth are incorporated, and threat modeling is used to evaluate and mitigate risks.
In the development phase, secure coding practices are implemented, and regular code reviews focus on identifying and resolving security issues early. The testing phase employs static and dynamic analysis tools, along with penetration testing, to uncover vulnerabilities. During deployment, secure configuration and environment hardening ensure that applications are protected.
Maintenance involves regular updates and continuous monitoring to detect and respond to incidents promptly. Finally, an incident response plan is crucial for effective communication and mitigation during security breaches, and continuous improvement based on feedback helps enhance security measures throughout the lifecycle. Integrating security at each stage ensures resilient applications that maintain user trust.
Conduct regular security audits and compliance checks :
- Key Security Tools to Use in the SDLC
- SAST (Static Analysis): SonarQube, Checkmarx, Fortify
- DAST (Dynamic Testing): Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP
- Penetration Testing: Metasploit, Kali Linux
- Code Review: GitHub Security, GitGuardian
- Monitoring & Logging: Splunk, ELK Stack, CloudWatch
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most critical security measure for business apps?
While all security measures are crucial, prioritizing data encryption, secure coding, and regular security assessments form the foundation of a safe business app.
2. How often should security audits be conducted?
Security audits should be conducted annually or more frequently, depending on the app’s exposure to sensitive data and regulatory requirements.
3. Can small businesses afford robust app security?
Many scalable security solutions cater to various budgets, ensuring that small businesses can implement adequate security measures.
4. What are the common types of security threats to business apps?
Malicious software designed to harm or exploit any programmable device, service, or network.
5. Is user authentication necessary for app security?
Absolutely. Strong user authentication, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), ensures that only authorized users can access the app.
6. How does regular software updating contribute to app security?
Regular updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities discovered since the last version, keeping the app more secure against new threats.
Conclusion
Security measures play a crucial role in protecting individuals, businesses, and digital assets from evolving threats. By implementing physical, cybersecurity, and network security strategies, organizations can prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and financial fraud. Strong security protocols, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, firewalls, and VPNs, enhance safety and ensure compliance with legal standards. As cyber threats continue to grow, continuous monitoring, employee awareness, and regular security updates are essential. A proactive approach to security safeguards sensitive information, maintains business continuity, and builds trust with customers and stakeholders, making security an indispensable part of modern life and digital transformation.