Solving the Global Resource Crisis: Strategies to Tackle the Challenge

In an era where the global population is skyrocketing, and our natural resources are depleting at an unprecedented rate, the urgency to address the looming global resource crisis cannot be overstated. The situation calls for collectively acknowledging our challenges and a concerted effort to implement solutions to steer us toward a sustainable future. This article aims to shed light on the complexities of tackling a global resource crisis, exploring its multifaceted impact on our planet and society, and delving into strategic measures that can mitigate its effects.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Global Resource Crisis
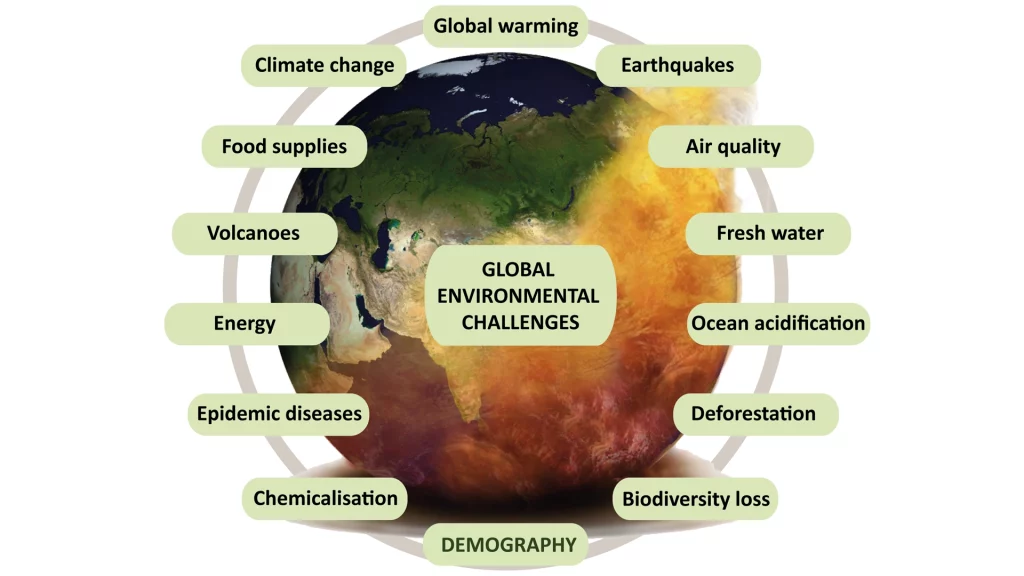
The global resource crisis is a multifaceted problem characterized by the alarming rate at which we are depleting the Earth’s natural resources. From fossil fuels to fresh water, the relentless demand for resources has led to a critical situation where the sustainability of our planet is at stake. The crisis is not just about the scarcity of resources but also concerns the degradation of ecosystems, loss of biodiversity, and the adverse effects of climate change. Our understanding of this crisis must be rooted in recognizing the interconnectedness of these issues and the need for a holistic approach to address them.

The situation we find ourselves in today did not happen overnight. It results from decades of unchecked industrial growth, unsustainable agricultural practices, and a global economy predicated on constant consumption. The effects of these practices are now becoming impossible to ignore, with climate change exacerbating the scarcity of water, food, and energy resources. Understanding the scope of this crisis is the first step toward formulating effective strategies to combat it.
The situation’s urgency requires us to rethink our approach to resource use. We must move away from the linear model of consumption that leads to waste and embrace a more circular economy where resources are reused and recycled. Furthermore, our understanding of the global resource crisis should compel us to consider the environmental implications and the social and economic dimensions. The crisis disproportionately affects the most vulnerable populations, who are often the least equipped to adapt to the changes it brings.
The Impact of the Resource Crisis on the Environment and Society
The global resource crisis has far-reaching implications that extend beyond environmental degradation. As the primary victim of resource depletion, the environment faces many challenges. Deforestation, soil erosion, water scarcity, and pollution are just a few manifestations of this crisis. These environmental issues threaten the natural habitats of myriad species and undermine the ecosystem services humans rely on for survival, such as clean air, water, and fertile land for agriculture.
The implications of the resource crisis are equally profound on a societal level. Resource scarcity has catalyzed global conflicts as nations and communities compete for dwindling water, land, and energy supplies. The crisis exacerbates social inequalities, with marginalized communities bearing the brunt of environmental degradation and resource scarcity. Food security is another critical issue, as the depletion of natural resources coupled with climate change impacts agricultural productivity, leading to food shortages and increased poverty.
The interconnectedness of environmental and societal issues highlights the complexity of the global resource crisis. It is not merely an ecological challenge but a comprehensive crisis that touches every aspect of human life. The impacts on society and the environment feed into each other, creating a vicious cycle difficult to break. Addressing this crisis requires a holistic approach that considers sustainability’s environmental, social, and economic dimensions.
Challenges in tackling the global resource crisis
Addressing the global resource crisis is fraught with challenges that stem from various sources. One of the primary obstacles is the political and economic structures that prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability. For instance, the global economy’s dependence on fossil fuels makes transitioning to renewable energy sources a complex endeavour. Furthermore, the globalized nature of the economy means that the actions of one country can have far-reaching impacts, complicating efforts to implement sustainable practices on a global scale.
Another challenge is the resistance to change from industries and sectors heavily invested in the current resource-intensive production model. The agricultural, mining, and manufacturing industries, in particular, need help adopting more sustainable practices due to the initial costs and adjustments required. The need for more awareness and understanding among the general public about the severity of the resource crisis and the need for sustainable consumption patterns compounds this resistance.
Technological limitations also pose a challenge in tackling the resource crisis. While technological advances have the potential to provide solutions, such as more efficient resource use and alternative energy sources, the pace of innovation and the scalability of these technologies often need to catch up to the growing demand for resources. The unequal distribution of technology and resources also exacerbates the divide between developed and developing nations, making it harder to implement global solutions to a worldwide crisis.
Strategies for resource conservation and sustainability
Some strategies can be employed to promote resource conservation and sustainability in the face of these challenges. One of the most critical steps is to shift towards a circular economy, where the life cycle of materials is extended through reuse, recycling, and recovery. This approach reduces waste and decreases the demand for new resources, alleviating pressure on the environment. Implementing circular economy principles requires changes at every production, consumption, and waste management level, necessitating collaboration between governments, industries, and consumers.
Another key strategy is the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices. Given agriculture’s significant impact on resource consumption and environmental degradation, transitioning to methods that minimize water use, reduce chemical inputs, and preserve soil health is essential. Precision farming, agroforestry, and organic farming can increase productivity while ensuring the long-term viability of agricultural resources.
Investing in green infrastructure is also crucial for resource conservation and sustainability. Green buildings, sustainable transportation networks, and renewable energy installations reduce the consumption of finite resources and mitigate the environmental impacts of urbanization and industrialization. These investments contribute to environmental sustainability, create jobs, and drive economic growth, demonstrating the feasibility of a sustainable financial model.
Promoting renewable energy sources
The transition to renewable energy sources is central to addressing the global resource crisis. Renewable energy, including solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Promoting renewable energy requires policy initiatives and technological innovation to overcome existing barriers to adoption.
Governments are critical in promoting renewable energy through incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks encouraging investment in clean energy projects. Policies such as feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards, and tax credits can make renewable energy more competitive with fossil fuels, driving the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
Technological innovation is also essential for advancing renewable energy. Improvements in the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy technologies can accelerate their adoption. Research and development efforts focused on energy storage, grid integration, and developing new materials for solar panels and wind turbines are crucial for overcoming the technical challenges associated with renewable energy.
Reducing waste and promoting recycling
Waste reduction and recycling are pivotal in tackling the global resource crisis. The generation of waste, mainly plastic waste, has significant environmental impacts, from polluting oceans and waterways to contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Promoting recycling and reducing waste at the source can alleviate these impacts and conserve valuable resources.
Efforts to reduce waste must focus on minimizing disposable products and packaging use, encouraging reusable and recyclable materials, and implementing waste sorting and collection systems that facilitate recycling. Public awareness campaigns and education programs can also play a crucial role in changing consumer behaviour and promoting a waste reduction and recycling culture.
Investments in infrastructure and technology that enable the efficient processing of recyclable materials must support recycling initiatives. Developing markets for recycled products is also essential for ensuring the economic viability of recycling programs. By turning waste into a resource, recycling can contribute to a circular economy and reduce the demand for new materials.
Implementing efficient resource management practices
Efficient resource management practices are essential for addressing the global resource crisis. These practices involve optimizing the use of resources throughout their lifecycle, from extraction and production to consumption and disposal. Implementing such practices requires a comprehensive approach that includes technological innovation, policy measures, and behavioural change.
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling efficient resource management. Advances in digital technology, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), can improve resource use efficiency in industries such as agriculture, manufacturing, and energy. Precision agriculture, for example, uses IoT devices to monitor soil moisture and nutrient levels, allowing for targeted irrigation and fertilization that reduce water and chemical use.
Policy measures are also critical for promoting efficient resource management. Regulations that set standards for resource efficiency, incentives for adopting sustainable practices, and penalties for excessive resource use can drive improvements in resource management. Policies that support research and development in sustainable technologies and practices can further enhance resource efficiency.
Behavioural change among consumers and businesses is another essential aspect of efficient resource management. Promoting sustainable consumption patterns, such as choosing products with a lower environmental impact and reducing energy use, can significantly reduce resource demand. Businesses can contribute by adopting sustainable practices in their operations and supply chains, such as energy efficiency measures and sustainable sourcing policies.
Encouraging sustainable consumption and production
Encouraging sustainable consumption and production is fundamental to tackling the global resource crisis. Sustainable consumption involves choosing products and services that have minimal environmental and societal impact. In contrast, sustainable production focuses on creating goods and services to conserve resources and minimize environmental damage. Promoting these principles requires a multifaceted approach that engages consumers, businesses, and governments.

Consumer awareness and education are crucial for encouraging sustainable consumption. Providing consumers with information about products and services environmental and social impacts can empower them to make more sustainable choices. Labelling schemes, such as eco-labels and fair trade certifications, can also guide consumers towards products that meet sustainability criteria.
Businesses have a significant role to play in promoting sustainable production. Adopting sustainable manufacturing, sourcing, and logistics practices can reduce the environmental footprint of products and services. Companies can also contribute by designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability, extending the lifecycle of products and reducing waste.
Governments can support sustainable consumption and production through policies and regulations. Implementing standards and rules that promote resource efficiency, reduce pollution, and encourage using sustainable materials can improve production practices. Incentives for sustainable business practices and consumer choices, such as tax breaks and subsidies, can further promote the adoption of sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Collaboration and international cooperation for resource conservation
The global nature of the resource crisis necessitates collaboration and international cooperation for effective resource conservation. Every nation must address the complex challenges of resource depletion and environmental degradation. Collaborative efforts, such as international agreements, joint research initiatives, and shared technology platforms, can facilitate sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices, enhancing the global response to the resource crisis.
International agreements and treaties are crucial in promoting resource conservation and environmental protection. Agreements such as the Paris Agreement on Climate Change and the Convention on Biological Diversity establish global targets and commitments for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving biodiversity, and promoting sustainable development. These agreements provide a framework for international cooperation and accountability, driving collective action on a global scale.
Joint research initiatives and technology sharing are also essential for advancing resource conservation. Collaborative research projects can accelerate the development of sustainable technologies and practices, leveraging the expertise and resources of multiple countries. Sharing technology and know-how, especially with developing countries, can help bridge the gap in technological capabilities, enabling all nations to implement resource conservation measures more effectively.
How is the global tech industry addressing resource shortages?
The global tech industry plays a pivotal role in addressing resource shortages through innovation and the development of sustainable technologies. From renewable energy and energy efficiency to water conservation and waste reduction, the tech industry is at the forefront of creating solutions that can mitigate the impacts of the resource crisis.
Renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines, are a prime example of how the tech industry is helping to address resource shortages. Materials science and engineering advances have dramatically reduced the cost of renewable energy, making it increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. The tech industry is also driving innovation in energy storage technologies, such as batteries and hydrogen fuel cells, which are crucial for overcoming the intermittency of renewable energy sources.
The tech industry is also contributing to water conservation by developing technologies that improve water use efficiency and enable water reuse and recycling. Intelligent irrigation systems, which use sensors and data analytics to optimize water use in agriculture, and water treatment technologies that allow for the reuse of industrial and municipal wastewater are examples of how technology can reduce water consumption and alleviate water shortages.
In the realm of waste reduction, the tech industry is developing solutions that promote recycling and the circular economy. Technologies such as materials recovery facilities, which automate the sorting and processing of recyclable materials, and platforms for the sharing and reusing of goods, are helping to reduce waste and conserve resources. The tech industry’s focus on designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability also contributes to waste reduction and resource conservation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are resource shortages in the global tech industry? Resource shortages refer to the limited availability of essential materials and components required for the manufacturing and operating of technological products. These shortages can include minerals, rare earth elements, energy sources, and water.
2. Why is addressing resource shortages important for the tech industry? Resource shortages can disrupt supply chains, increase production costs, and hinder innovation in the tech sector. Additionally, if not managed effectively, they can contribute to environmental degradation and social instability. Addressing these shortages is crucial for maintaining sustainable growth and competitiveness in the industry.
3. How is the global tech industry mitigating resource shortages? The tech industry is employing various strategies to reduce resource shortages. These include:
- It invests in research and development to find alternative materials and technologies that reduce reliance on scarce resources.
- We implement efficient resource management practices, such as recycling, reusing, and refurbishing components and products.
- She is collaborating with governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders to promote responsible sourcing and sustainable extraction of raw materials.
- Developing innovative business models, such as product-as-a-service and sharing platforms, to prolong product lifespans and reduce resource consumption.
4. What role does innovation play in addressing resource shortages? Innovation is essential for addressing resource shortages in the tech industry. By developing new materials, technologies, and processes, companies can reduce the demand for scarce resources and create more sustainable products. Innovation also improves efficiency, allowing companies to do more with fewer resources.
5. How are supply chain disruptions affecting resource availability in the tech industry? Supply chain disruptions, such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics, can exacerbate resource shortages in the tech industry by interrupting the flow of materials and components. To mitigate these risks, companies diversify their supply chains, stockpile critical materials, and adopt digital technologies for real-time monitoring and resilience planning.
6. What are some examples of tech companies leading the way in addressing resource shortages? Several tech companies are proactively addressing resource shortages and promoting sustainability. For example:
- Apple has committed to using 100% recycled or renewable materials in all its products and packaging.
- Google has pledged to operate on carbon-free energy by 2030 and invest in renewable energy projects worldwide.
- Tesla is developing advanced battery technologies to reduce reliance on rare earth elements and accelerate the transition to electric vehicles.
- IBM is leveraging blockchain technology to trace the origin of raw materials and ensure ethical sourcing practices in its supply chain.
7. How can consumers contribute to addressing resource shortages in the tech industry? Consumers can contribute to addressing resource shortages by making informed purchasing decisions and supporting companies prioritizing sustainability and responsible sourcing. They can also extend the lifespan of their devices through repair, refurbishment, and recycling programs and advocate for policies that promote resource conservation and circular economy principles.
8. What are the potential challenges and barriers to addressing resource shortages in the tech industry? Some possible challenges and obstacles to addressing resource shortages include:
- Economic constraints, such as the cost of implementing sustainable practices and technologies.
- Technical limitations, such as the availability of viable alternatives to scarce resources.
- Regulatory hurdles, including inconsistent standards and enforcement mechanisms across different regions.
- Sociopolitical factors, such as geopolitical tensions and trade conflicts, can disrupt supply chains and resource markets.
9. How do resource shortages in the tech industry intersect with broader environmental and social issues? Resource shortages in the tech industry are closely linked to broader environmental and social problems, such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and human rights violations. Addressing these shortages requires a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic factors and prioritizes the well-being of people and the planet.
10. What are some future trends and developments in addressing resource shortages in the tech industry? Future trends and developments in addressing resource shortages may include:
- She continued materials science and technology innovation to develop sustainable alternatives to scarce resources.
- Greater integration of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, to optimize resource use and minimize waste.
- They increased collaboration and partnerships across industries and sectors to tackle complex supply chain challenges and promote resource stewardship.
- This has increased consumer awareness and demand for products and services that are environmentally friendly, socially responsible, and ethically sourced.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of how the global tech industry addresses resource shortages and the challenges and opportunities associated with this critical issue.
Conclusion: Working together to solve the global resource crisis
Tackling the global resource crisis requires a collective effort that spans nations, industries, and communities. The strategies discussed in this article, from promoting renewable energy and reducing waste to implementing efficient resource management practices and encouraging sustainable consumption, offer a roadmap for addressing the challenges of resource depletion and environmental degradation. Collaboration and international cooperation are essential for amplifying the impact of these strategies, enabling a coordinated global response to the resource crisis.
The tech industry’s role in developing sustainable technologies and innovations underscores the potential for human ingenuity to overcome the challenges of resource scarcity. By harnessing the power of technology, we can find solutions that not only mitigate the impacts of the resource crisis but also drive economic growth and improve the quality of life for people worldwide.
As we move forward, we all must play our part in addressing the global resource crisis. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to implement the strategies outlined in this article, making sustainable choices that protect our planet for future generations. By embracing a spirit of cooperation and innovation, we can overcome the challenges of resource depletion and build a sustainable, prosperous future for all.
In conclusion, solving the global resource crisis is within our reach. Understanding the issue’s complexities requires a concerted effort, adopting sustainable practices, and working together across borders and sectors. The strategies and actions we take today will determine our planet’s health and future generations’ well-being. Let’s commit to working together to solve the global resource crisis for our sake and for the sake of those who will come after us.