Unlocking the Power of Privacy: An Overview of Virtual Private Networks
In our digital age, the quest for privacy and security online has never been more paramount. With cyber threats lurking around every corner of the internet and surveillance efforts intensifying worldwide, safeguarding our digital footprint is a necessity. This brings us to the cornerstone of digital privacy and security: Virtual Private Networks, or VPNs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the nitty-gritty of VPNs, exploring their workings, benefits, common uses, and much more. Let’s embark on this journey to unlock the power of privacy that VPNs offer.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
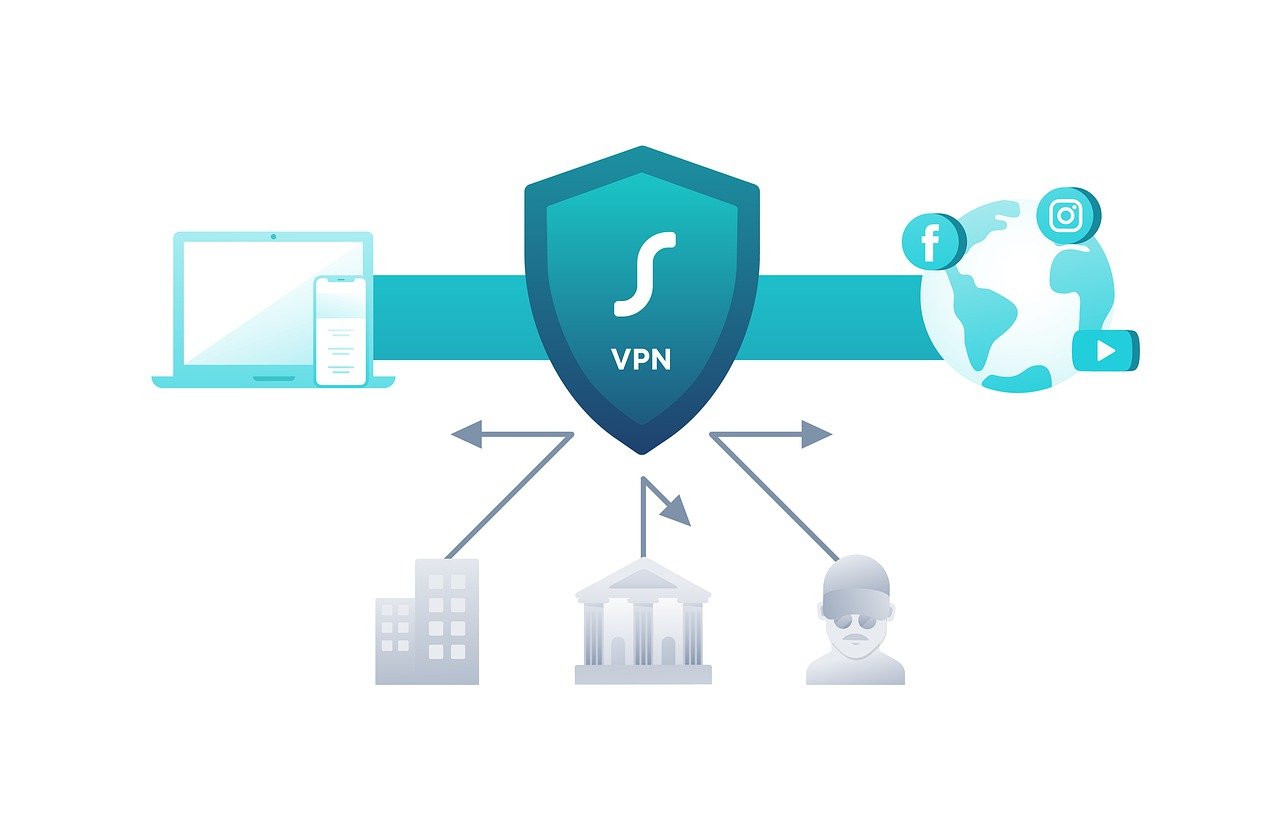
The concept of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) might seem complex at first glance, but at its core, it’s a powerful tool designed to offer users privacy and security online. A VPN is essentially a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. This tunnel encrypts your online data, making it incomprehensible to anyone who might intercept it, thus safeguarding your online activities from prying eyes.
The inception of VPN technology dates back to 1996 when a Microsoft employee developed the Peer to Peer Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). The primary aim was to create a secure and private connection between computers over the internet. Since then, the technology has evolved tremendously, incorporating robust encryption methods and protocols to ensure an impregnable shield around users’ online communications.
Today, VPNs are more than just a tool for tech-savvy individuals. They have become an essential component of online privacy and security for everyday internet users. Whether it’s for securing your data on a public Wi-Fi network, accessing geo-restricted content, or simply keeping your browsing history private, VPNs offer a versatile solution to a myriad of online challenges.
How Does a VPN Work?
Understanding how a VPN works is crucial to appreciating its significance in our digital lives. When you connect to a VPN service, it assigns your device a temporary IP address, masking your real IP address. This process, known as IP masking, is the first step towards achieving online anonymity.
Once the connection is established, the VPN creates an encrypted tunnel for your data to travel through. Encryption is a process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Even if someone were to intercept your data, they would only see gibberish without the encryption key.
The encrypted data then reaches the VPN server, where it is decrypted and sent to its final destination. This journey ensures that your online activities are hidden from your Internet Service Provider (ISP), potential hackers, and even government surveillance.
Benefits of Using a VPN
The benefits of using a VPN extend beyond just privacy and security. Firstly, VPNs help in bypassing geo-restrictions and censorship. By connecting to a server in a different country, you can access content that may be restricted in your region. This feature is particularly useful for journalists, researchers, and the general populace living in countries with stringent internet censorship.
Secondly, VPNs are indispensable for secure communication, especially on unsecured Wi-Fi networks like those in airports, cafes, and hotels. Public Wi-Fi networks are notorious for being breeding grounds for cyber threats. Using a VPN on these networks encrypts your data, protecting it from potential cyber-attacks.
Lastly, VPNs contribute to a more open and free internet. In an era where net neutrality is under threat, VPNs offer a way to escape bandwidth throttling and discrimination by ISPs. This ensures that all websites and online services have an equal opportunity to reach their audience without unjustified delays or blocked access.
Common Use Cases for VPNs
VPNs have a wide array of use cases, catering to different needs and objectives. One of the most common reasons people turn to VPNs is for accessing geo-blocked content. Streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer offer different libraries of shows and movies based on your geographical location. With a VPN, you can connect to a server in a country where the content is available, thus bypassing these restrictions.

Another prevalent use case is for securing communications over public Wi-Fi networks. Business travelers and digital nomads often find themselves relying on public Wi-Fi. A VPN ensures that their sensitive information, such as emails, passwords, and financial details, remains encrypted and out of reach from cybercriminals.
Furthermore, VPNs are used for maintaining anonymity online. For individuals living in countries with oppressive regimes, this can be a matter of safety. VPNs help activists, whistleblowers, and journalists protect their identity while sharing critical information with the world.
Choosing the Right VPN Provider
With the plethora of VPN providers available, choosing the right one can be daunting. The key factors to consider include the provider’s privacy policy, the number of server locations, speed, and security features. A no-logs policy is crucial, as it ensures that the provider does not store any data about your online activities.
The variety and location of servers are also vital. A provider with a vast network of servers across different countries offers more options for bypassing geo-restrictions and ensures better speeds. Speaking of speeds, VPNs can sometimes slow down your internet connection due to the encryption process. Opting for a provider known for its high-speed connections can mitigate this issue.
Security features to look out for include strong encryption methods, IP leak protection, and a kill switch. A kill switch is a safety feature that disconnects your device from the internet if your VPN connection drops, preventing any data leaks.
Setting Up and Configuring a VPN
Setting up and configuring a VPN is generally straightforward, thanks to user-friendly apps provided by most VPN services. The first step is to choose a VPN provider and subscribe to their service. Once subscribed, you’ll need to download and install the VPN application on your device.

Upon launching the app, you’ll be prompted to log in with your credentials. Following login, you can usually connect to a server with just one click. However, for specific needs, you might want to manually select a server location. Most VPN apps offer customization options, allowing you to tweak the settings to your preference, such as choosing a VPN protocol or setting up a kill switch.
VPN Security and Privacy Features
VPN security and privacy features are the backbone of what makes VPNs so valuable. Encryption is at the heart of these features, with most reputable VPNs employing AES-256 encryption – the same standard used by governments and security experts worldwide.
IP leak protection ensures that your real IP address is never exposed while connected to the VPN. This feature guards against DNS, IPv6, and WebRTC leaks that could reveal your identity. The aforementioned kill switch is another critical security feature, providing an emergency stop to protect your data in case the VPN connection fails.
VPN Protocols and Encryption Methods
VPN protocols determine how data is routed from your device to the VPN server. Common protocols include OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPsec, and WireGuard. Each protocol has its strengths and weaknesses in terms of speed, security, and compatibility. For instance, OpenVPN is praised for its high security and compatibility across devices, while WireGuard is known for its speed and simplicity.

Encryption methods, on the other hand, define how your data is encrypted. AES-256 is the gold standard, offering robust security without significantly impacting speed. Some VPNs also offer proprietary encryption methods designed to enhance security or speed further.
VPN Troubleshooting and Best Practices
Even with the best VPN services, you might encounter issues such as slow speeds, connection drops, or difficulties accessing certain websites. Troubleshooting these issues often involves simple steps like switching servers, changing VPN protocols, or checking for app updates. Ensuring your VPN software is up to date is crucial for both security and performance.
Adhering to best practices can also enhance your VPN experience. This includes using a wired connection for better speeds, regularly changing servers to avoid congestion, and avoiding simultaneous connections from multiple devices unless necessary.
What are the Fundamentals of Virtual Private Networks and How Do They Secure Online Activity?
The fundamentals of VPNs revolve around creating a secure and private connection over the internet. This is achieved through IP masking, data encryption, and routing data through secure servers. By doing so, VPNs protect your online activity from surveillance, cyber threats, and unwanted scrutiny.
Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct decryption key. Secure VPN protocols define the rules for data transmission, ensuring that data travels securely from your device to the VPN server and onwards to its final destination.
Conclusion: The Power of Privacy with VPNs
Virtual Private Networks are a cornerstone of online privacy and security in today’s digital world. They provide a robust solution to a wide array of challenges, from safeguarding data on public Wi-Fi networks to bypassing internet censorship. By understanding how VPNs work, their benefits, and how to choose the right provider, users can significantly enhance their online privacy and security.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of the internet, the significance of VPNs cannot be overstated. They empower us to reclaim our right to privacy and protect our digital lives from the myriad of threats lurking online. Embracing the power of VPNs is a step towards a more secure and private online experience.