Addressing the Global Lithium Shortage: Innovative Solutions for a Sustainable Future
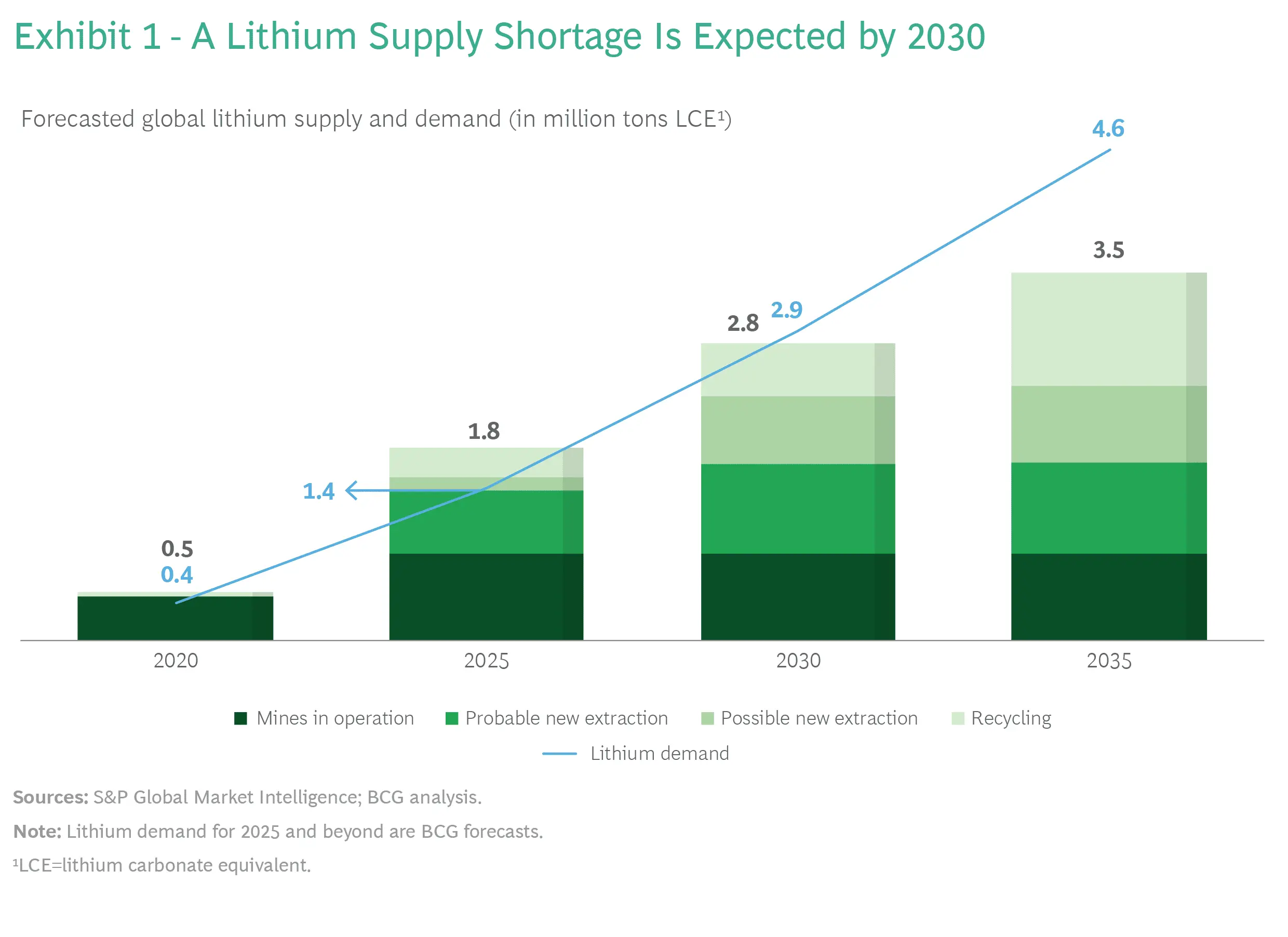
As we move towards a more sustainable future, the demand for lithium, a crucial element in the production of batteries, has surged. The global lithium shortage has become a pressing issue, with implications for various industries, including electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and portable electronics. In this article, I will delve into the causes and consequences of the lithium shortage, highlighting the importance of finding innovative solutions to address this challenge.
The primary cause of the global lithium shortage is the rapid growth of the electric vehicle market. As governments and consumers shift towards clean energy alternatives, the demand for electric vehicles has skyrocketed. Electric vehicle manufacturers heavily rely on lithium-ion batteries, which require a significant amount of lithium. This surge in demand has outpaced the current production capacity of lithium, leading to a supply deficit.
The consequences of the lithium shortage are far-reaching. The limited availability of lithium has resulted in price hikes, making it more expensive for companies to produce batteries. This, in turn, affects the affordability and accessibility of electric vehicles and clean energy storage solutions. Additionally, the shortage has created a bottleneck in the supply chain, hindering the growth of the sustainable energy sector. We must address this issue promptly to ensure a sustainable and green future.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Lithium in the Sustainable Energy Sector

Lithium is pivotal in the sustainable energy sector, particularly in producing lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are crucial for electric vehicles and storing renewable energy generated from sources like solar and wind. Storing energy efficiently is essential for grid stability and the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources.
With the increasing shift towards renewable energy, the demand for lithium-ion batteries is expected to surge even further. The use of lithium-ion batteries extends beyond transportation and renewable energy storage. They are also used in portable electronics, such as smartphones and laptops, contributing to the overall demand for lithium. Finding innovative solutions to address the lithium shortage is imperative to sustain the growth of the sustainable energy sector and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Current Solutions for Addressing the Lithium Shortage
Various strategies and solutions have been implemented to alleviate the supply deficit in response to the global lithium shortage. One approach is to increase lithium production by developing new mines and extraction methods. Traditional lithium extraction methods, such as brine and hard rock mining, have limited resource availability and environmental impact. Therefore, lithium extraction and production innovations are crucial to meet the growing demand.

One promising innovation is the development of lithium extraction technologies from unconventional sources, such as geothermal and oilfield brines. These alternative sources can supplement traditional lithium production, reducing the strain on existing reserves. Furthermore, advancements in lithium recycling technologies can also help alleviate the shortage. By recovering lithium from used batteries and other electronic waste, we can reduce the demand for new lithium production and minimize waste.
Exploring Alternative Sources of Lithium
To address the lithium shortage sustainably, it is essential to explore alternative sources of lithium beyond traditional mining. One such source is lithium extraction from seawater. Seawater contains a vast amount of lithium, and innovative technologies are being developed to extract it efficiently. The advantage of seawater extraction is that it is virtually inexhaustible and does not require extensive mining operations, minimizing environmental impact.
Another alternative source of lithium is the recovery of lithium from unconventional mineral deposits. Lithium can be found in various minerals, including spodumene, petalite, and lepidolite. Developing technologies to extract lithium from these mineral deposits efficiently can diversify the lithium supply chain and reduce reliance on limited resources.
The Role of Recycling in Solving the Lithium Shortage
Recycling lithium from used batteries and electronic waste is crucial to addressing the lithium shortage. Only a tiny percentage of lithium-ion batteries are recycled, significantly losing valuable resources. By implementing efficient recycling processes, we can recover lithium and other valuable materials, reducing the demand for new lithium production.
Recycling lithium-ion batteries involves several steps, including collection, disassembly, and separation of materials. Advanced technologies are being developed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of these processes. Additionally, incentivizing battery recycling and establishing proper collection systems can increase recycling rates and ensure the recovery of valuable resources.
Government Policies and Initiatives to Address the Lithium Shortage
Governments worldwide have recognized the importance of addressing the lithium shortage and have implemented various policies and initiatives to promote sustainable lithium production and usage. These policies encourage investment in lithium mining, research and development, and recycling infrastructure.

Some governments have implemented subsidies and tax incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. These measures not only stimulate demand but also create a favorable environment for the growth of the lithium industry. Additionally, governments can play a crucial role by fostering international collaborations to share knowledge and resources, accelerating progress towards sustainable lithium solutions.
Collaborative Efforts Between Countries and Companies
The global lithium shortage is a complex issue that requires collaborative efforts between countries and companies. International collaborations facilitate sharing resources, technologies, and expertise, accelerating the development and implementation of innovative solutions.
Countries rich in lithium reserves can collaborate with countries facing shortages to establish trade agreements and promote sustainable lithium production. This collaboration can ensure a reliable supply chain while minimizing the environmental impact of lithium extraction. Furthermore, companies can engage in research and development partnerships to drive technological advancements in lithium extraction, production, and recycling.
The Future of Lithium and Sustainable Energy
The future of lithium and sustainable energy depends on our ability to effectively address the global lithium shortage. As the demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy continues to rise, finding innovative solutions to meet this demand sustainably is crucial.
Advancements in lithium extraction, production, and recycling technologies hold promise for alleviating the lithium shortage. Exploring alternative sources of lithium, such as seawater and unconventional mineral deposits, can diversify the supply chain and reduce reliance on limited resources. Additionally, government policies and collaborative efforts between countries and companies are essential to drive progress in the lithium industry.
How Is the Tech Industry Addressing the Lithium Shortage?
The tech industry significantly addresses the lithium shortage by investing in research and development to find alternative battery technologies. While lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market, companies are exploring new battery chemistries, such as solid-state and sodium-ion batteries, which can reduce the reliance on lithium.
Solid-state batteries offer advantages such as higher energy density, improved safety, and shorter charging times. By replacing the liquid electrolyte found in lithium-ion batteries with a solid-state electrolyte, these batteries can provide a viable alternative for energy storage. Similarly, sodium-ion batteries utilize sodium, which is more abundant and widely available, as an alternative to lithium.
Conclusion
The global lithium shortage poses a significant challenge as we strive for a sustainable future. Understanding the causes and consequences of this shortage is crucial for finding innovative solutions. By investing in research and development, exploring alternative sources of lithium, and promoting recycling, we can address the lithium shortage sustainably.
Government policies and collaborative efforts between countries and companies are essential for driving progress in the lithium industry. Furthermore, the tech industry’s exploration of alternative battery technologies can reduce the reliance on lithium and pave the way for a more diverse and sustainable energy storage landscape.
Solving the lithium shortage requires a multifaceted approach encompassing technological advancements, international collaborations, and conscious consumption. By addressing this challenge head-on, we can ensure a sustainable future powered by clean energy and efficient energy storage systems.





